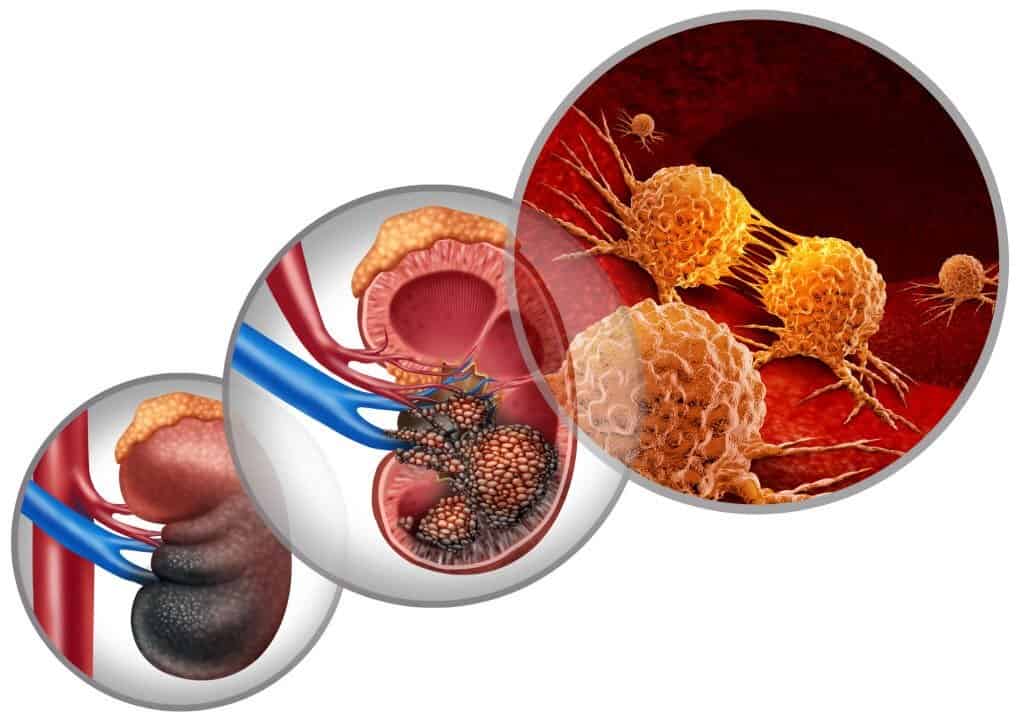
Renal cell carcinoma (RCC) is a type of advanced kidney cancer. It affects the tubules or little tubes in the kidneys. These tubules are responsible for filtering and cleaning blood. They produce urine and excrete waste from the body. Urine passes through the ureter and into the bladder. The urine then leaves the body through the urethra. In patients with RCC, malignant cells form in the tubules. Common symptoms include blood in the urine, pain in the side, and weight loss.
Who Are at Risk for KidneyCancer?
There are certain factors that can make a person more at-risk for RCC. Just because you have risk factors, it doesn’t mean that you will get cancer. Your doctor will still determine if you are at risk.
- Obesity
- Family history of RCC
- Genetic conditions
- Hypertension
- Smoking
- Misuse of medication
What Is Fotivda (Cancer med)?
Fotivda is an approved treatment for renal cell carcinoma. It is prescribed to patients who tried at least two medicines that didn’t work. It may also be given if immunotherapy does not work. Several studies prove the effectiveness of Fotivda in controlling cancer cells. Subjects showed tumor shrinkage. Fotivda slows down the progress. It belongs to a class of medicine known as kinase inhibitors. These work by stopping the growth of cancer cells.
How to Use Fotivda (Cancer med)
Before starting on Fotivda, make sure to inform your doctor of your medical history. It is important to tell them of any conditions you may have. These include kidney, liver, and heart problems. Remember to take affordable Fotivda exactly as prescribed to you. The usual dose of Fotivda is once a day for 21 days. This is followed by a 7-day break from treatment. Fotivda with or without food in the stomach. Do not break or chew the capsules. Do not take less or more than prescribed.
How to Store Fotivda (Cancer med)?
Fotivda must be stored in its original container and not in a pill box. This medication must be stored at room temperature and in a dry place. Keep the container sealed, and do not use the medication beyond its expiration date.
Side Effects of Fotivda (Cancer med)
The more common side effects of Fotivda (Cancer med) USA can include:
- Vomiting
- Nausea
- Fever
- Chills
- Fatigue
- Yellowing of skin
- Dark urine
- Loss of appetite
- Abdominal pain
- Rashes
- Shortness of breath
- Cough
- Fast heartbeats
- Blurry vision
These side effects may go away within a few days or a couple of weeks. If they’re more severe or don’t go away, talk to your doctor or pharmacist. Serious side effects from Fotivda (Cancermed) aren’t common, but they can occur.
Commonly Asked Questions About Fotivda (Cancer med)
Can you buy Fotivda (Cancer med) from Canada?
Yes, you may buy Fotivda (Cancer med) online in Canada through your trusted online pharmacy partner, USA Script Helpers. At USA Script Helpers, we are committed to providing you with quality medication in a convenient and hassle-free manner. You may also buy Fotivda (Cancermed) without Medicare from us.
Do you need a prescription for Fotivda (Cancer med)?
Yes, Fotivda (Cancer med) is a medication that requires a prescription. You may submit a digital copy of your prescription to us by uploading it directly to the website or sending it to us through email or fax. Once we have your prescription on file, we can process your order. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions on how to submit a prescription to USA Script Helpers.
Can Americans buy Fotivda (Cancer med) from Canada?
Yes, people in the United States may buy Fotivda (Cancermed) with USA Script Helpers through our easy-to-use Canadian pharmacy website. Simply search for Fotivda (Cancer med), then proceed to the check-out process, and send your prescription to us. USA Script Helpers are very reliable
in providing prescription drugs and non-prescription drugs to Americans.